Invited Speakers
Dr. Soufiane Haddout
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ibn Tofail University, MoroccoSpeech Title: Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Sebou Estuary, Moroccan Atlantic coast
Abstract: This presentation analyzed heavy metals: iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), and lead (Pb) on surface sediments and evaluated the role of sediment grain size and organic carbon (OC) in the distribution of metals. Sixteen numbers of surface sediment samples were collected during summer period of 2019 from Sebou estuary (Morocco). The dominance of fine-grained sediments (clay and silt) was noted in the study region. The organic carbon distribution indicates that they are brought in the surroundings of coastal areas. Correlation analysis clearly indicates that fine particles and organic carbon control the distribution of metals. The correlation coefficient for relationships between the metals shows a strong degree of association between the fine fractions. The significant correlations were evident for Zn and Mn (r=0.66), Mn and Fe (r=0.70). The correlations between OC versus Mn (r=0.80), OC and sand (r=-0.70), OC versus silt (r=0.96), OC and clay (r=0.87) were significant. The degree of correlation between metals and other major constituents is often used to indicate the origin of the metals. On the other hand, contamination levels of metals were examined by using geo-accumulation index (I geo ), and contamination factor (CF) which indicated the fact that the heavy metals were unpolluted to moderately polluted in the estuarine sediments.

Prof. Na Liu
Department of Ecology, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, ChinaSpeech Title: Catalytic Performance and Mechanism of Biochars for Dechlorination of Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons in Sulfide Aqueous Solution
Abstract: Biochars (BCs) have been investigated as a natural and economical activator to treat organic contamination. Compared with commercial carbon materials, BCs have a better prospect of large-scale application. For the first time, this study certified degradation of tetrachloroethene (PCE),trichloroethylene (TCE) and hexachloroethane (HEC) in sulfide-containing aqueous solutions catalyzed by BCs pyrolyzed at different temperatures. Interestingly, BC800 could catalyze PCE, TCE, HEC and dechlorination and form acetylene and chloride ion with over 99 % nontoxic transformation in neutral and alkaline pH conditions. Furthermore, materials surface properties, BC dosages and sulfide concentrations were considered as limiting factors for dechlorination, and the last one had the strongest influence. XPS analysis demonstrated that catalytic ability of BC was attributed to pyridine nitrogen (N6) on surface, because C and O adjacent to N6 strongly favor nucleophilic reactions. These results evaluated the applicability of degrading toxic chlorinated alkenes mediated by natural carbon materials in sulfide-containing environment
Prof. Guoxing Sun
Institute of Applied Physics and Materials Engineering, University of Macau, ChinaSpeech Title: Application of Nano-Foam Concrete in Prefabricated Products and Cast-In-Place Projects
Abstract: The speaker will use two examples of industrialized technology inventions to describe how to effectively combine and apply the two different disciplines of chemistry and civil engineering to the research and development of various composite materials, and talk about the stories of commercializing the research products. (1) Use cement as raw material to produce nanoparticles (size <5 nm), and use them to prepare a series of hydrogels with super elasticity, adsorption and water swelling properties, and develop their applications in engineering, electronics, biological materials, environment and other fields. (2) Low-cost, nanoparticle-stabilized foam that can keep stable for years, which could be used to mix with cement paste to prepare lightweight, high-strength, fire-resistant and thermally insulated foam cement. The product was widely used in fabricated lightweight wall panels for energy-efficient buildings.
Dr. Nethaji N
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government Polytechnic College, IndiaSpeech Title: Efficiency Enhancement of Solar PV Panel by Incorporating Wickless Loop Heat Pipes with Plate Type Evaporator
Abstract: With the advancement of civilization and hence the energy consumption, the need for exploring novel energy sources is also on the rise. Solar power generation is one of the fastest developing en-ergy sectors in the world. The conversion efficiency of a solar cell decreases with increase in the temperature of the junctions. Our research study focuses to reduce the junction heat by incorpora-tion of Loop Heat Pipes with Plate type Evaporator (WLHP-PE) to transport the heat generated from the panel to the ambient. The study showed that the temperature of the panel is reduced by 5 to 9 ºC. A rolled bond evaporator plate is attached to the bottom of the panel which acts as evapora-tor part of Loop Heat Pipe (WLHP-PE). Acetone, which is the working medium, filled in the WLHP-PE in liquid state to the required level to absorb the heat generated at the bottom of the pan-el and becomes vapour. This vapour transports the heat to the condenser section of the loop heat pipe, which is immersed in water bath. There the heat it is rejected to the water due to which the working medium is again converted to liquid state. For the given operating conditions, the conver-sion efficiency of PV module is increased by 10 to 12 % without any external power supply.
Prof. Xiaoyu Liu
Huazhong Agricultural University; Key Laboratory of Environment Correlative Dietology, Ministry of Education, ChinaSpeech Title: The Test of Toxic Effect of Phoxim on Crucian Carp (Carassius Auratus Gibelio) by Using HE Staining, SEM and TEM Approach
Abstract: The toxic effect of phoxim on crucian carp (carassius auratus) was investigated via Hematoxylin-Eosin staining (HE) combined with Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) observation. The results of morphology identified by HE staining, SEM and TEM demonstrated that certain concentration phoxim could induce pathological damage of liver (drug metabolism organ), gill- (respiratory organ) and brain (nervous system) in crucian carp at tissue and cell level at different degree. The morphology results was more and more clear and persuasive with the approach used becoming more and more advanced from HE staining to SEM then to TEM. The experimental setup included a blank control group and a phoxim exposure group with semi static poisoning method. The exposure concentration was set to two dosage groups: high dose (0.33mg/L) and low dose (0.083 mg/L) with exposure time of 40 days and 60 days, respectively. Under these conditions, the HE staining observation results, as well as the SEM and TEM observation results were listed below: Compared with the control group, the liver, gills, and brain of crucian carp were damaged from pathology and morphology under the action of phoxim. The appearance of liver of crucian carp damaged was a disordered arrangement of liver cells, with honeycomb like damage and cell rupture; The appearance of gill of crucian carp damaged was: large area of epithelial cells shedding and cell deformation; The appearance of brain of crucian carp damaged was: the neurons in the hippocampus were loose and disordered, the neuronal body was deformed, some cell nuclear membranes were broken, and the nucleus was dissolved. The degree of damage to various parts showed a dose-effect relationship and a time-dependent relationship. The damaged effects of phoxim on the liver, gills, and brain tissues of crucian carp may be one of the mechanisms underlying its toxic effects on crucian carp and it is necessary for further research.
Dr. Qian Wang
Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Guangdong Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, China;Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Technion, Israel
Speech Title: Chemical Mapping of Phosphorus (P) in Sewage Sludge throughout Wastewater Treatment Plants for Efficient P Recovery
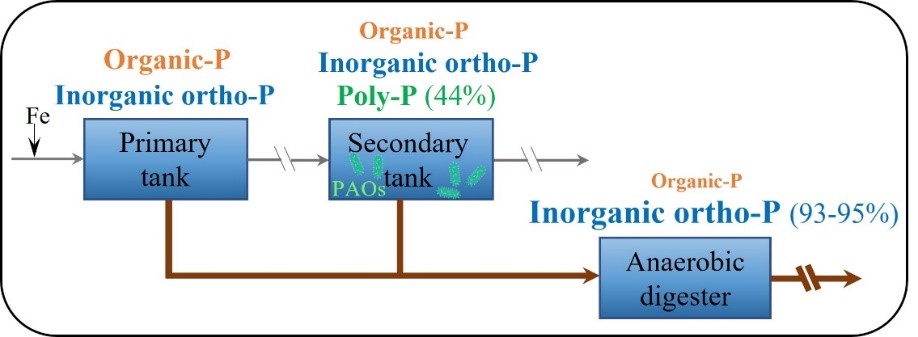
Abstract: Phosphorus (P) is a necessary element for all living organisms. However, phosphate rock, the primary source of P, is finite and will be depleted in a century. This makes it urgent to recover P from secondary sources, e.g., wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). To provide insights into efficient P recovery from WWTPs, this study mapped the P speciation in the sludge throughout three WWTPs in Denmark, i.e., Ejby Mølle, Billund, and Esbjerg WWTPs. Our recently validated sequential P extraction protocol, which can quantify vivianite Fe3(PO4)2·8H2O, was combined with a suite of analytical techniques such as optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). At Ejby Mølle WWTP, which used Fe-dosing chemical P removal and enhance biological P removal (EBPR), the primary sludge comprised of comparable inorganic orthophosphate (ortho-P, 53% of total P) and organophosphate (organic-P, 45%). The secondary sludge contained abundant polyphosphate (poly-P, 44%) formed by poly-P accumulating organisms during EBPR. However, the biogenic P (poly-P and organic-P) was degraded after anaerobic digestion, making inorganic ortho-P the dominated P in the downstream sludge (93-95%) with a bit organic-P. Fe-P, i.e., vivianite-P and Fe(III)-P, was the main inorganic ortho-P in all sludge samples, and it increased from 46% to 71% of total P by anaerobic digestion. Vivianite, a promising P recovery product which can be recovered from sludge by magnetic separation, was observed in the sludge after anaerobic digestion at high quantity with PXRD reflections (10-11 mg-P/g, 37-39% of total P). It was also found in all other sludge samples by microscopy and chemical extraction but not detected by PXRD. The PXRD amorphous properties of these vivianite particles may cause their overlook in sludge in previous studies. Similar trends of P variation were observed throughout Billund and Esbjerg WWTPs; but Al-P (P sorbed to amorphous Al hydroxides) was a P mineral phase as dominant as Fe-P (both 38%) in the downstream sludge at Esbjerg WWTP, which co-dosed Al and Fe.
Dr. Jingwei Ma
Department of Water Engineering and Science, Hunan University, ChinaSpeech Title: Granular Activated Carbon as Fluidized Cathode to Enhance Electro-Fermentation for Caproate Production
Abstract: The rapid consumption of fossil energy has caused increasingly serious energy shortage and environmental pollution problems worldwide, which also poses extra burden to carbon neutrality, and led to a frontier and hot issue aiming to realize the sustainable development of the environment and energy demand. A growing number of researchers have focused on the production of high-value biofuels from organic waste, such as ethanol and fatty acids, which are also precursors of renewable fuels and chemicals and deserve wider applications. Medium chain fatty acids (MCFA) production via chain elongation (CE) of carboxylic acids through a reversed β-oxidation pathway has been a great interest recently. MCFA have more excellent physical properties than volatile fatty acids (VFA) and methane with 6–12 C atoms, and the high hydrophobicity contribute to further processing and separation. Electro-fermentation (EF) is the application of bio-electrochemical system in traditional anaerobic fermentation, which can use inexhaustible and cheap cathode instead of hydrogen/ethanol/lactate as electron donor. Caproate production from volatile fatty acids (VFAs) through chain elongation processes in electro-fermentation is a sustainable and promising technique for organic waste recycling and resources recovery. However, the small surface area of working electrode is one of the main factors impeding the improvement of performance. Therefore, fluidized cathode via granular activated carbon (GAC) dosage was employed in this study to stimulate the electro-fermentation for enhanced caproate generation, and the relevant mechanism was revealed. Herein, the effects of different filling ratios of GAC (0, 3, 8, 13, and 18%) on electro-fermentation with three different types of electron donors (lactate, lactate and cathode, and cathode) were investigated. It proved that the cathode could serve as the sole electron donor in the fluidized cathode EF systems, which outcompeted lactate, and lactate and cathode with easier availability and higher cost effectiveness. Results showed that the fluidized cathode electro-fermentation systems achieved the best performance at a GAC filling ratio of 8% with cathode as the sole electron donor. The yield of caproate, carbon recovery rate and electron recovery rate were 2.1, 1.8 and 1.6 times higher than those without GAC, respectively. The electrochemical analysis also verified the highest electrochemical activity of the cathode biofilm and the relatively small internal resistance of the system. It was noted that the dominant bacteria on the cathode biofilm shifted from Lactobacillus to Clostridia, Oscillibacter and Caproiciproducens, which probably contributed to the caproate production via chain elongation process. This work would provide some insights into application of electro-fermentation for high value added caproate production.
Prof. Thomas Lei
Institute of Science and Environment, University of Saint Joseph, ChinaSpeech Title: Statistical Forecast of Pollution Episodes in Macao during National Holiday and COVID-19
Abstract: Statistical methods such as multiple linear regression (MLR) and classification and regression tree (CART) analysis were used to build prediction models for the levels of pollutant concentrations in Macao using meteorological and air quality historical data to three periods: (i) from 2013 to 2016, (ii) from 2015 to 2018, and (iii) from 2013 to 2018. The variables retained by the models were identical for nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) but not for ozone (O3). Air pollution data from 2019 was used for validation purposes. The model for the 2013 to 2018 period was the one that performed best in the prediction of the next-day concentrations levels in 2019, with a high coefficient of determination (R2) between predicted and observed daily average concentrations (between 0.78 and 0.89 for all pollutants), and low root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and biases (BIAS). To understand if the prediction model was robust to extreme variations in pollutants concentration, a test was performed under the circumstances of a high pollution episode for PM2.5 and O3 during 2019 and a low pollution episode during the period of implementation of the preventive measures for the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding the high pollution episode, the period of the Chinese National Holiday of 2019 was selected, in which high concentration levels were identified for PM2.5 and O3, with peaks of daily concentration exceeding 55 µg/m3 and 400 µg/m3, respectively. The 2013 to 2018 model successfully predicted this high pollution episode with high coefficients of determination (0.92 for PM2.5 and 0.82 for O3). The low pollution episode for PM2.5 and O3 was identified during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic period, with a low record of daily concentration for PM2.5 levels at 2 µg/m3 and O3 levels at 50 µg/m3, respectively. The 2013 to 2018 model successfully predicted the low pollution episode for PM2.5 and O3 with a high coefficient of determination (0.86 and 0.84, respectively). Overall, the results demonstrate that the statistical forecast model is robust and able to correctly reproduce extreme air pollution events of both high and low concentration levels.








